if y(x) is solution to differential equation xy’ -ln x =0, with y(1) = 7/2, find y(e)
Published 3 years ago • 255 plays • Length 3:29Download video MP4
Download video MP3
Similar videos
-
 2:00
2:00
find the differential of each function.(a)y = x^(2)sin(8x) (b)y = ln(4 t^2)
-
 3:52
3:52
use separation of variables to solve initial value problem dy/dx = (4sqrt(y) ln x)/x; y=1, when x=e
-
 8:44
8:44
pre-u: integration by part - integrate lnx and x^2lnx
-
 0:43
0:43
take the derivative of the natural log function
-
 4:19
4:19
calculus help: differential equations: (1 lnx y/x)dx (-1 lnx)dy=0 - integration factor
-
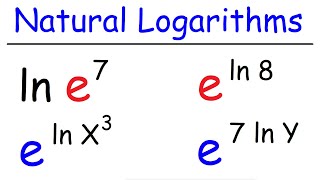 2:49
2:49
natural logarithms
-
 2:00
2:00
calculus help: separable differential equations - y^'=e^(-x 4lny) - techniques
-
 2:23
2:23
solve equations, ln(x 3) = 2 and 100e^(2x) =600. natural logarithms and exponential equations
-
![solving d[(ln x)^2] / dx.](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/UGQa7VaS00Q/mqdefault.jpg) 0:50
0:50
solving d[(ln x)^2] / dx.
-
 2:35
2:35
calculus 1: ch 5.1 derivative of e^x and lnx (7 of 24) why is the derivative of e^x e^x?
-
 3:50
3:50
calculus 1: ch 5.1 derivative of e^x and lnx (8 of 24) why is the derivative of ln(x)=1/x?
-
 7:25
7:25
calculus help: homogeneous - differential equations - ( x-y lny y lnx) dx x( lny-lnx )dy=0
-
 5:51
5:51
derivative of x to the power of ln(x) times a constant
-
 2:31
2:31
derivative of f(x) = ln(x^4 1) - 4e^(x/2) - x
-
 2:03
2:03
calculus 1: ch 5.1 derivative of e^x and lnx (2 of 24) more rules on logarithms
-
 5:17
5:17
use infinite series to find the limit of ln(x)/(x - 1) as x approaches 1
-
 7:19
7:19
derivatives - ln(x) - chain rule - quick and easy
-
 3:21
3:21
find a differential equation whose solution is y = a*ln(bx)
-
![determine if the function f(x, y) = x[ln(sqrt(x^2 y^2) - ln(y)] y*e^(x/y) homogeneous?](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/6UiTQAXBKUc/mqdefault.jpg) 8:32
8:32
determine if the function f(x, y) = x[ln(sqrt(x^2 y^2) - ln(y)] y*e^(x/y) homogeneous?