(ii) electrocardiographs are often connected as shown in fig. 19-68. the lead wires to the legs are…
Published 1 month ago • 13 plays • Length 0:33Download video MP4
Download video MP3
Similar videos
-
 0:33
0:33
(ii) electrocardiographs are often connected as shown in fig. 19-68. the lead wires to the legs are…
-
 0:33
0:33
fill in the blank. the equation r=2 cosθrepresents a _____.
-
 0:33
0:33
use demoivre’s theorem to find the indicated power of the complex number. write answers in rectangu…
-
 13:59
13:59
evaluating cardiac axis on 12 lead electrocardiogram - right, left, or normal?!
-
 0:33
0:33
no and cl_2 is proportional to the product of the concentrations of the two gases: […
-
 37:51
37:51
understanding egms at a glance - interpreting cardiac electrograms
-
 13:08
13:08
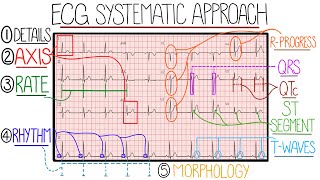
ecg interpretation made easy (learn how to interpret an ecg in 13 minutes)
-
 36:37
36:37
cardiac axis determination
-
 0:33
0:33
(iii) (a) determine the currents i_1 , i_2 , and i_3 in fig. 19-61. assume the internal resistance …
-
 0:33
0:33
the standard reduction potentials of the following half-reactions are given in appendix e: \begina…
-
 3:18
3:18
eegdigitrack cfm/aeeg - diagnostic and monitoring
-
 11:14
11:14
cardiac arrest during an eeg
-
 15:21
15:21
the cardiac axis made ridiculously easy
-
 4:32
4:32
sensing and electrograms
-
 0:32
0:32
two independent rhythms on an electrocardiographic recording
-
 0:33
0:33
graph each spiral of archimedes. see example 7. r=θ(use both positive and nonpositive values.)
-
 29:09
29:09
what is an electrophysiologist and when should you see one?
-
 7:30
7:30
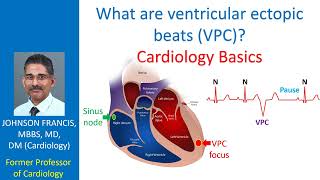
what are ventricular ectopic beats (vpc)? cardiology basics
-
 0:33
0:33
in exercises 25-28, use the given graphs of x=f(t) and y=g(t) to sketch the corresponding parametri…
-
 1:11
1:11
what is an electrophysiologist? (evgueni fayn, md)
-
 3:01
3:01
calibrate gamry reference 3000 ae