let u = 3x^2y and v = xz^2 - 2y. evaluate grad[(grad u) â· (grad v)].
Published 1 month ago • 1 view plays • Length 0:33
Download video MP4
Download video MP3
Similar videos
-
 5:09
5:09
261.10.6 what can a three-variable gradient ∇f(x,y,z) tell us?
-
 3:57
3:57
calculus 3: line integrals (35 of 44) condition 2 for independence
-
 6:03
6:03
calc 3 ch.14 finding approximate change | differentials | given changes in independent variables
-
 2:59
2:59
evaluate grad f if f=logx^2 y^2 z^2 | find grad∅ if ∅=logx^2 y^2 z^2 #uvduduli
-
 9:57
9:57
integrating with t-results (2 of 3): changing the variable of integration
-
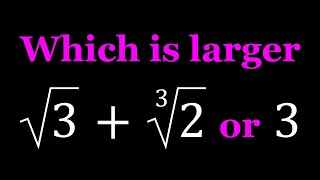 8:30
8:30
comparing sqrt(3) cbrt(2) and 3 | suggested by juan pablo
-
 11:26
11:26
integration tricks (that teachers won't tell you) for integral calculus
-
 13:34
13:34
gradient and directional derivative | mit 18.02sc multivariable calculus, fall 2010
-
 1:59
1:59
calculus 3: vector calculus in 3-d (2 of 35) vector between 2 points
-
 4:53
4:53
integral test to evaluate series, ex 3
-
 3:07
3:07
pc unit 3 how to evaluate for sine using the unit circle for an angle larger than 2pi
-
 3:47
3:47
how to find the gradient of f(x,y,z)=x**2 y**3 z**4
-
 6:04
6:04
solve a differential equation by substitution, v=x^3 y^3, an exam question
-
![calculus 3: line integrals (18 of 44) what is a line integral? [(y)dx (z)dy (x)dz] example 6](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/vTRQzlrVAn8/mqdefault.jpg) 5:03
5:03
calculus 3: line integrals (18 of 44) what is a line integral? [(y)dx (z)dy (x)dz] example 6
-
 2:46
2:46
finding the gradient of a multivariate function z = sin(x^2 y^2) at (-3, 4)
-
 2:17
2:17
finding the gradient of a multivariate function w = 3x^2 2y^3 6z at (1, 2, 3)
-
 2:49
2:49
calculus 3: ch 2.1 lines and vectors in 3-d (9 of 20) find the equation of a line: ex. 1
-
 2:14
2:14
calculus 2: infinite sequences and series (34 of 62) finding con- or di-vergence: ex. 2/3
-
 3:19
3:19
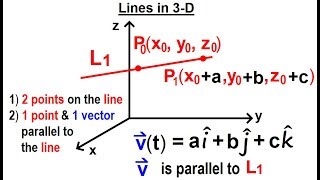
calculus 3: ch 2.1 lines and vectors in 3-d (6 of 20) lines in 3-d
-
 8:46
8:46
linear modelling (3 of 3: using the gradient to find a relation between two variables)
-
 3:52
3:52
evaluate a line integral of x^3y^2 with respect to x (differential form)
-
 4:37
4:37
mathematical singularity in 3 dimensions demystified
Clip.africa.com - Privacy-policy
 5:09
5:09
 3:57
3:57
 6:03
6:03
 2:59
2:59
 9:57
9:57
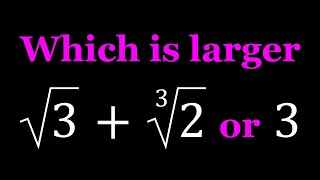 8:30
8:30
 11:26
11:26
 13:34
13:34
 1:59
1:59
 4:53
4:53
 3:07
3:07
 3:47
3:47
 6:04
6:04
![calculus 3: line integrals (18 of 44) what is a line integral? [(y)dx (z)dy (x)dz] example 6](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/vTRQzlrVAn8/mqdefault.jpg) 5:03
5:03
 2:46
2:46
 2:17
2:17
 2:49
2:49
 2:14
2:14
 3:19
3:19
 8:46
8:46
 3:52
3:52
 4:37
4:37